40 FACTS ABOUT MIXTURES
40 FACTS ABOUT MIXTURES
BY: PJ MIANA
_________________________________________________
The following are the facts about mixtures:
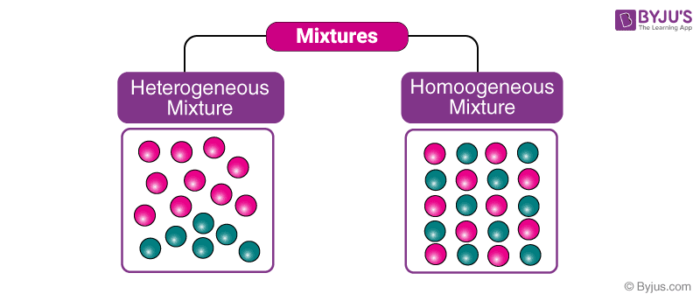
- A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. They are also called solutions.
- A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. They are also called suspensions.
- Homogeneous mixtures can be either solid, liquid, or gas.
- Heterogeneous mixtures can also be either solid, liquid, or gas.
- Examples of homogeneous mixtures include air, salt water, vinegar, liquid solutions, gas solutions, and solid solutions.
- Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include salad, chocolate chip cookies, sand, colloids, suspensions, and emulsions.
- Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform appearance throughout.
- Heterogeneous mixtures have a non-uniform appearance throughout.
- Homogeneous mixtures cannot be separated by physical means, but it may be difficult or impossible to do so.
- Heterogeneous mixtures can be separated by physical means, such as filtration, sieving, or centrifugation.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often used in cooking and cleaning.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often used in construction and manufacturing.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often used in medicine and biology.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often used in art and decoration.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often used in science experiments.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often used in everyday life.
- The components of a homogeneous mixture cannot be distinguished by the naked eye.
- The components of a heterogeneous mixture can be distinguished by the naked eye.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often clear or transparent.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often cloudy or opaque.
- Homogeneous mixtures are also called solutions.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are also called suspensions.
- Homogeneous mixtures can be classified as liquid solutions, gas solutions, and solid solutions.
- Heterogeneous mixtures can be classified as colloids, suspensions, and emulsions.
- Liquid solutions are homogeneous mixtures of a liquid solvent and a solute.
- Gas solutions are homogeneous mixtures of a gas solvent and a solute.
- Solid solutions are homogeneous mixtures of a solid solvent and a solute.
- Colloids are heterogeneous mixtures of a dispersed phase and a dispersion medium.
- Suspensions are heterogeneous mixtures of a dispersed phase and a dispersion medium in which the particles are large enough to be visible.
- Emulsions are heterogeneous mixtures of two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often used in cooking, such as when salt is added to water to make a brine solution.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often used in construction, such as when concrete is made from cement, sand, gravel, and water.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often used in medicine, such as when saline solution is used to flush an injured eye.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often used in art, such as when oil paint is mixed with other materials to create different colors and textures.
- Homogeneous mixtures are often used in science experiments, such as when a solution of sugar and water is used to measure the boiling point of water.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are often used in everyday life, such as when salad dressing is used to dress a salad.
- The properties of a homogeneous mixture are the same throughout the mixture.
- The properties of a heterogeneous mixture may vary from one part of the mixture to another.
- The components of a homogeneous mixture can be separated by physical means, but it may be difficult or impossible to do so.
- The components of a heterogeneous mixture can be separated by physical means, such as filtration, sieving, or centrifugation.

Comments
Post a Comment