[Q3] ENERGY TRANSFER
Exploring
the Transformation of Energy: Sound, Heat, Light, and ElectricityBy: Pj Miana
Introduction:
Energy is all around us, and it can take many forms. In this lesson, we'll delve into how different types of energy—sound, heat, light, and electricity—can be transformed from one form to another. Understanding these transformations helps us comprehend the world and the technology we use every day.
1. Sound
Energy:
Sound energy is produced by vibrations traveling through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. It can be transformed in various ways:
- Mechanical to Sound: When an object vibrates, it creates sound waves. For example, when you pluck a guitar string, the mechanical energy of your hand's motion is transformed into sound energy.
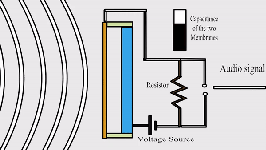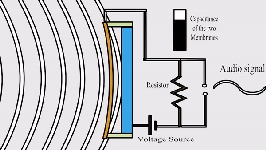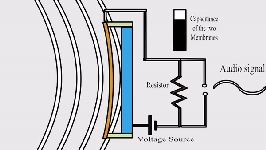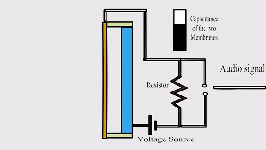
- Sound to
Electrical: Microphones transform sound waves into electrical signals. These
signals can then be amplified and converted back into sound through speakers.
2. Heat
Energy:
Heat energy is the energy that flows between objects of different temperatures. It can also be transformed in multiple ways:
- Chemical to
Heat: Burning fuel, such as wood or gas, releases chemical energy, which is
transformed into heat energy. This process is how we heat our homes and cook
our food.
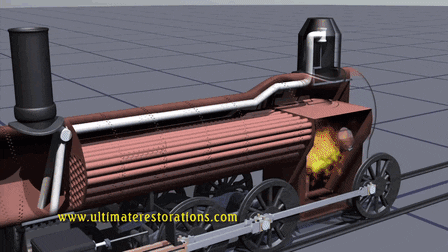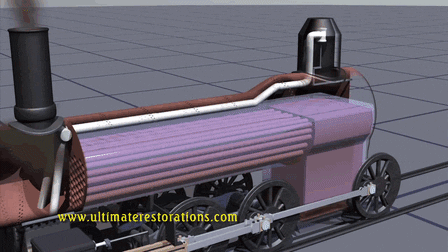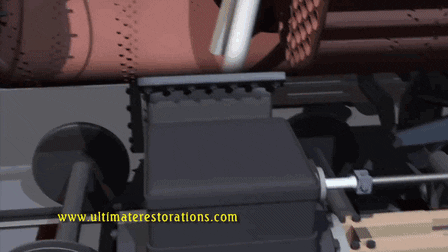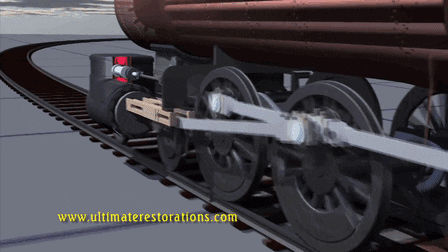
- Heat to
Mechanical: Steam engines and turbines use heat energy to produce mechanical
work. Steam is created by heating water, which expands and drives pistons or
turbines.
3. Light
Energy:
Light energy is produced by vibrations of electromagnetic radiation. It too can undergo transformations:
- Electrical to
Light: Light bulbs and LEDs transform electrical energy into light energy. When
an electric current passes through the filament of a bulb, it heats up and
emits light.
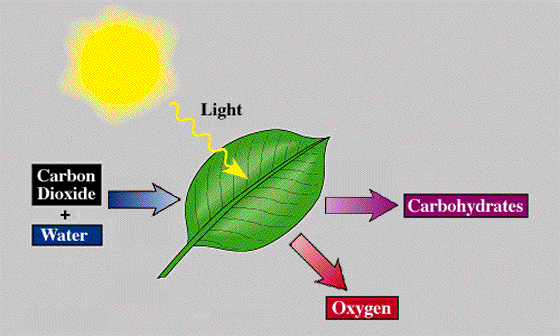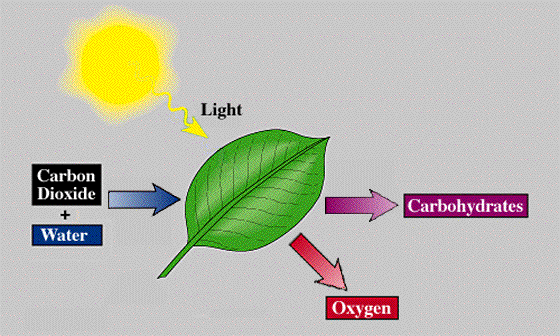
- Light to Chemical: Photosynthesis in plants converts light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in the form of glucose. This process is vital for plants to produce food.
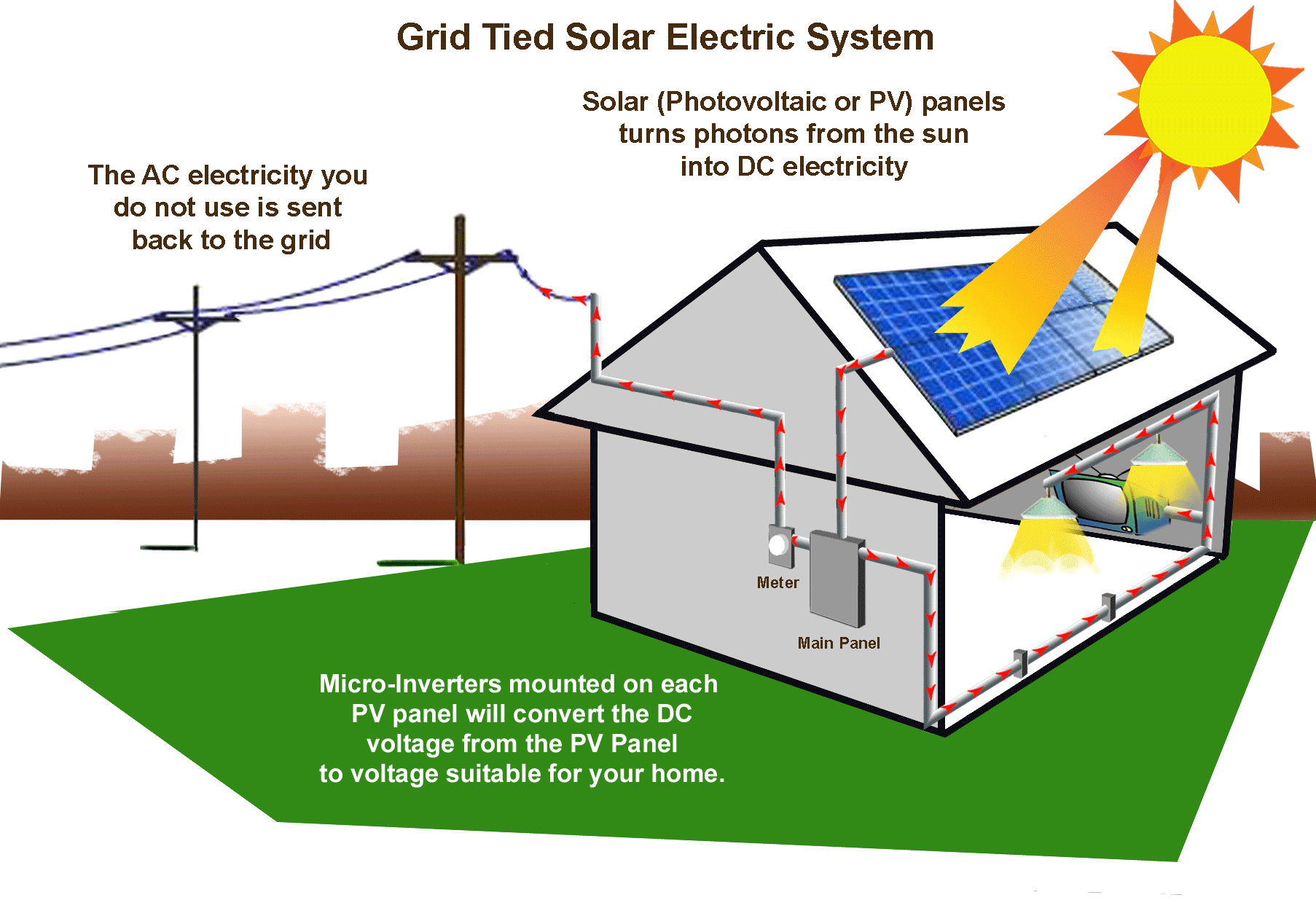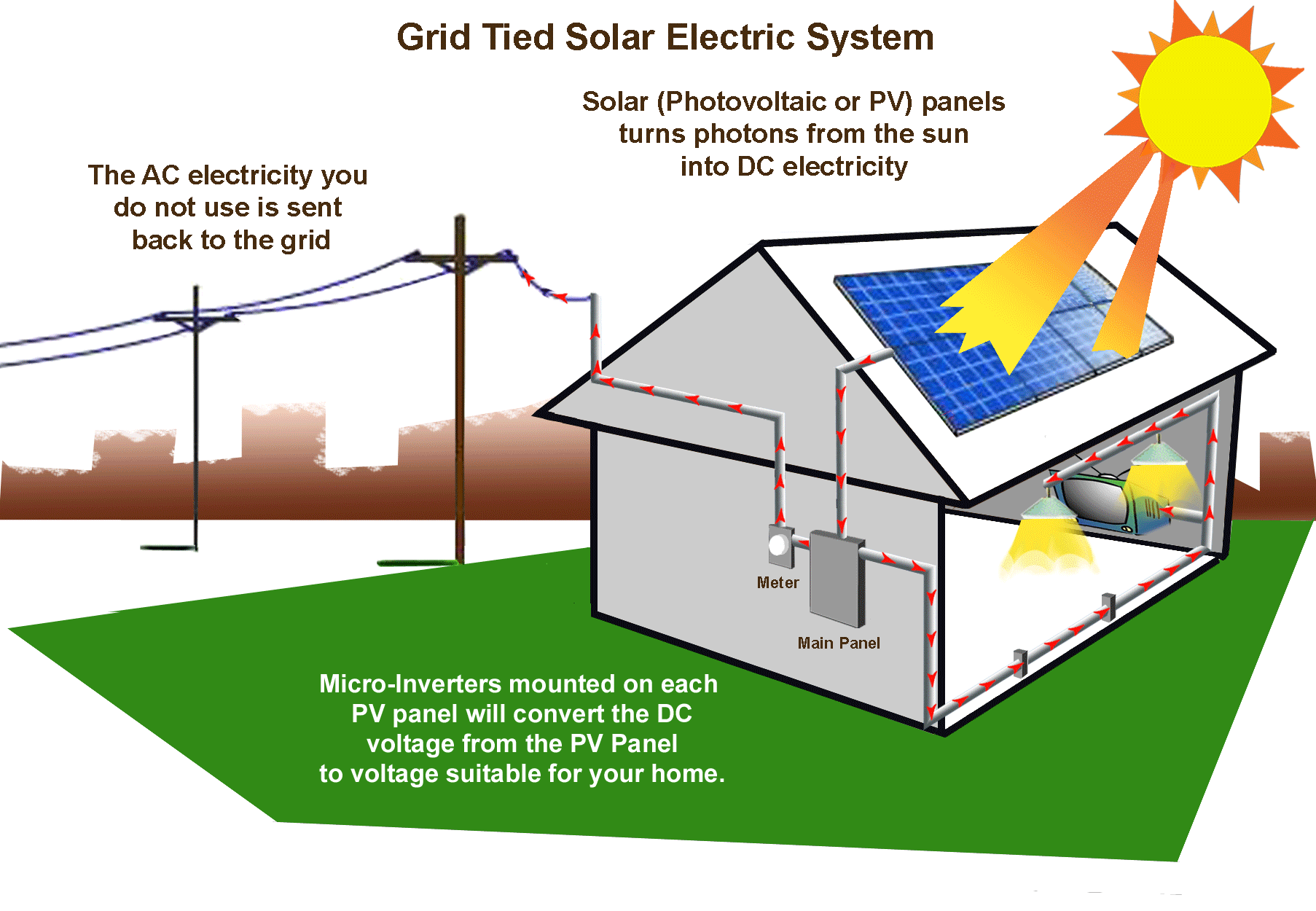
- Light to Electrical: Devices like the photovoltaic cells or solar panels convert the light of the sun to electrical energy.
4. Electrical Energy:
Electrical energy is the movement of electrons through a conductor. It's perhaps the most versatile form of energy, capable of various transformations:
- Mechanical to Electrical: Generators convert mechanical energy, such as the rotation of turbines or the movement of water in hydroelectric dams, into electrical energy.
- Electrical to
Heat: Electric heaters and stoves transform electrical energy into heat energy,
warming up their surroundings or cooking food.
- Electrical to Sound - Electricity can be used to create sound. Examples of this is the sound produced by the speakers of your appliances like radios, TVs, Bluetooth speakers, etc.
Conclusion:
Understanding how energy can be transformed from one form to another is essential for technological advancements and everyday life. Whether it's the sound of music, the warmth of sunlight, the glow of a light bulb, or the power running our devices, energy transformations shape our world. By grasping these concepts, we gain insight into the interconnectedness of different forms of energy and how they sustain our existence and drive innovation. Keep exploring the fascinating world of energy transformations—it's an electrifying journey!








Comments
Post a Comment