SCIENCE 6 SPELLING BEE REVIEWER QUARTER 2 WEEK 1 AND WEEK 2
SCIENCE 6
SPELLING BEE REVIEWER
QUARTER 2
WEEK 1 AND WEEK 2
MELC:
·
Explain how the organs of each organ system work
together 6LT-IIa-b-1
-Muskulo-skeletal System and The Integumentary System
1.
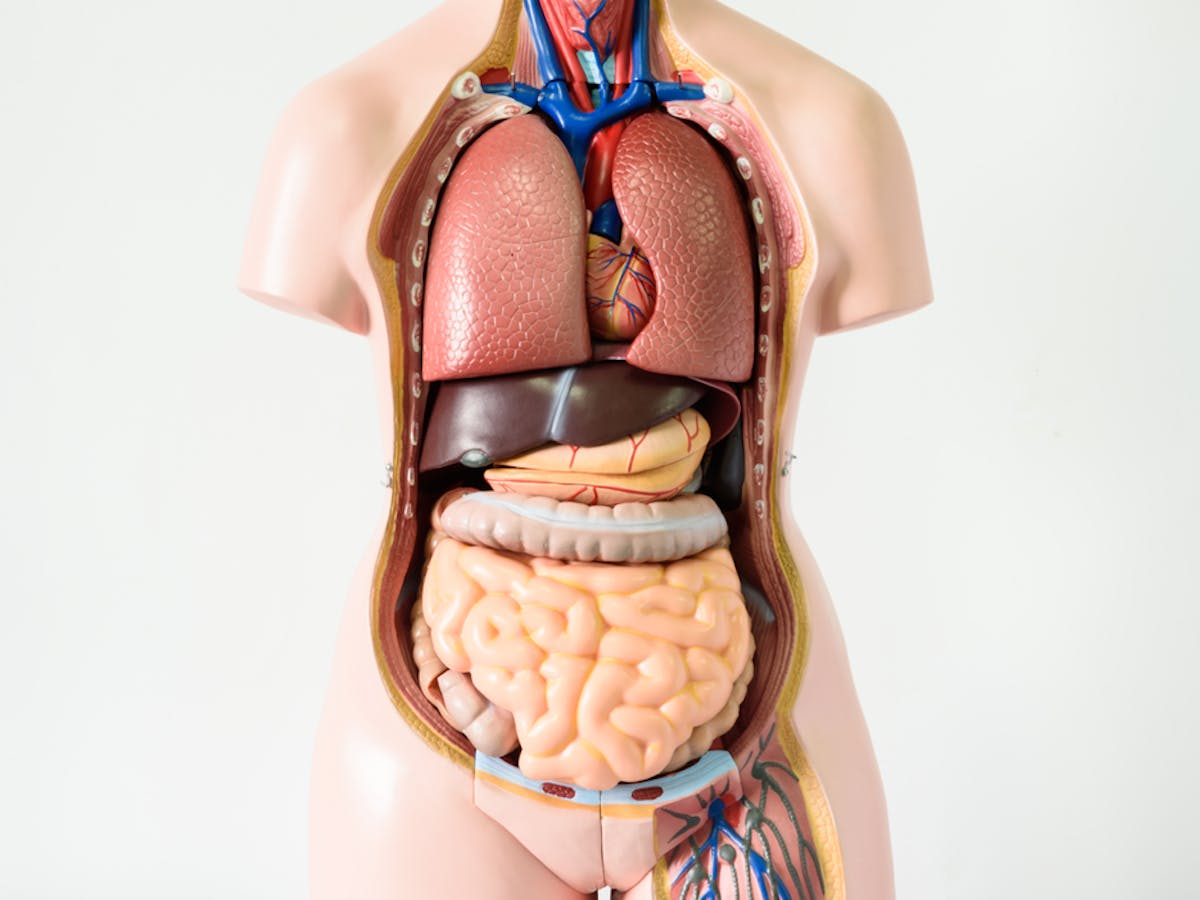
STOMACH
/ stuh·muhk/
·
The stomach is a muscular, sac-like organ
located in the upper part of the abdomen, between the esophagus and the small
intestine. Its primary function is to break down and digest food that has been
swallowed, through the secretion of acid and enzymes.
2.
INTESTINES
/ in·teh·stnz/
·
The intestines are a part of the digestive
system, consisting of the small intestine and the large intestine. The small
intestine is a long, narrow tube that is responsible for the majority of
nutrient absorption from the food we eat.
3.
CARTILAGE
/ kaar·tuh·luhj/
·
Cartilage is a flexible
connective tissue found in various parts of the body, such as the nose, ears,
joints, and ribcage. It is made up of specialized cells called chondrocytes and
a matrix of collagen and proteoglycans.
4.
PHALANGES
/ fuh·lan·jeez/
·
Phalanges are the bones that
make up the fingers and toes. They are long, slender bones that are connected
to the metacarpal bones in the hands and the metatarsal bones in the feet.
5.
VERTEBRAE
·
Vertebrae are the individual
bones that make up the spinal column, also known as the backbone. They provide support to the body, protect the spinal cord
and nerves, and allow for movement and flexibility of the spine.
6.
LIGAMENTS
/ li·guh·muhnts/
·
Ligaments are tough, fibrous
bands of connective tissue that connect bones to other bones, providing
stability and support to the joints. They are made up of collagen fibers and
are found throughout the body, connecting bones in the spine, arms, legs, and
other areas.
7.
MUSCLES
/ muh·slz/
·
Muscles are specialized
tissues in the body that are responsible for movement, stability, and
maintaining posture. There are three types of muscles in the body: skeletal,
smooth, and cardiac.
8.
APPENDICULAR
/ a·puhn·di·kyuh·lr/
·
The appendicular skeleton is the portion
of the skeleton that includes the bones of the limbs (arms and legs), as well
as the bones that connect them to the axial skeleton (the bones of the skull,
spine, and ribcage). The appendicular skeleton also includes the bones of the
pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) and pelvic girdle.
9.
SEBACEOUS
/ suh·bay·shuhs/
·
Sebaceous glands are small,
oil-producing glands found in the skin of mammals, including humans. They are
most commonly found on the face, scalp, chest, and back. Sebaceous glands are
responsible for producing sebum, a natural oil that helps to lubricate and protect
the skin and hair.
10.
INTEGUMENTARY
/in·teg·yuh·men-tuh-ree/
·
The integumentary system is the organ
system that includes the skin, hair, nails, and various glands associated with
them. Its primary functions are to protect the body from external damage,
regulate body temperature, and provide sensory information to the brain.
11.
ECCRINE
/ eh·kruhn/
·
Eccrine glands are sweat
glands that are found all over the body, but are most numerous on the palms,
soles of the feet, and forehead. They are responsible for producing watery
sweat, which is composed mostly of water and salt, and helps to regulate body
temperature by evaporating on the skin's surface.
12.
APOCRINE
/ a·puh·kruhn/
·
Apocrine glands are a type of
sweat gland that are primarily found in the armpits and genital region. Unlike
eccrine glands, which produce watery sweat, apocrine glands produce a thicker,
milky sweat that is rich in proteins and lipids.
13.
SQUAMOUS
/ skway·muhs/
·
Squamous cells are a type of
flat, scale-like cells that are found in many tissues throughout the body,
including the skin, lungs, and lining of the digestive and reproductive
systems. They are named for their flat, thin shape, which allows them to easily
form a protective barrier.
14.
MELANOCYTES
/ muh·la·nuh·sites/
·
Melanocytes are specialized cells
found in the skin, hair, and eyes that produce and contain a pigment called
melanin. Melanin gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes, and also provides
protection against harmful UV radiation from the sun.
15.
LYMPH
/ limf/
· Lymph is a clear, watery fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system, which is a network of vessels and organs that work together to remove excess fluid, waste products, and harmful substances from the body.
Comments
Post a Comment